Getting started
Getting started with nteract¶
This user guide prepares you for setting up the basics of the nteract notebook app.The nteract ecosystem supports Jupyter notebooks, one of the most popular interactive notebook formats. Interactive notebooks are a great tool for data scientists, hobbyists, and programmers looking to document their code, experiment with models, generate visualizations, and prototype code.
Setting up the nteract desktop application¶
Download the desktop application on your machine for the fastest way to get started with nteract. Find the installer for your operating system on the nteract homepage. Once downloaded and installed, launch nteract from the install directory.
NOTE: This guide uses the nteract desktop application as the reference point.
Setting up using Snap¶
Snapcraft is compatible with all the major Linux distros. Learn more about Snaps from the Getting started documentation, and download it for your distro from the install page.
After installing Snap, use the code below to begin installing nteract.
Example:
$ sudo snap install nteract --edge
Setting up the nteract web application¶
Open, create, and edit notebooks as well in the web app. Use nteract within your web browser by installing the nteract_on_jupyter Python package using the command below.
Example:
$ pip install nteract_on_jupyter
From here, run Jupyter with the nteract extension installed using the following command. This opens to the nteract web interface in your default browser.
$ jupyter nteract
Install the following examples separately by navigating to the directory and running the code below. This example uses a Command Prompt window.
$ git clone https://github.com/nteract/examples
$ cd examples
How to create a new notebook¶
By default, the nteract app opens to a new, empty notebook. If using the command line, the nteract command creates or opens a notebook directly.
$ nteract --kernel ${insert kernel name here}
Alternatively, open a notebook by either double clicking on the notebook file on your machine or selecting File > Open from the nteract menubar.
Writing code in interactive notebooks¶
New notebooks in nteract launch with an empty code cell. Write any executable code in this code cell.
NOTE: Code must be written in the language of the kernel that you are connected to in order to execute.
Example:
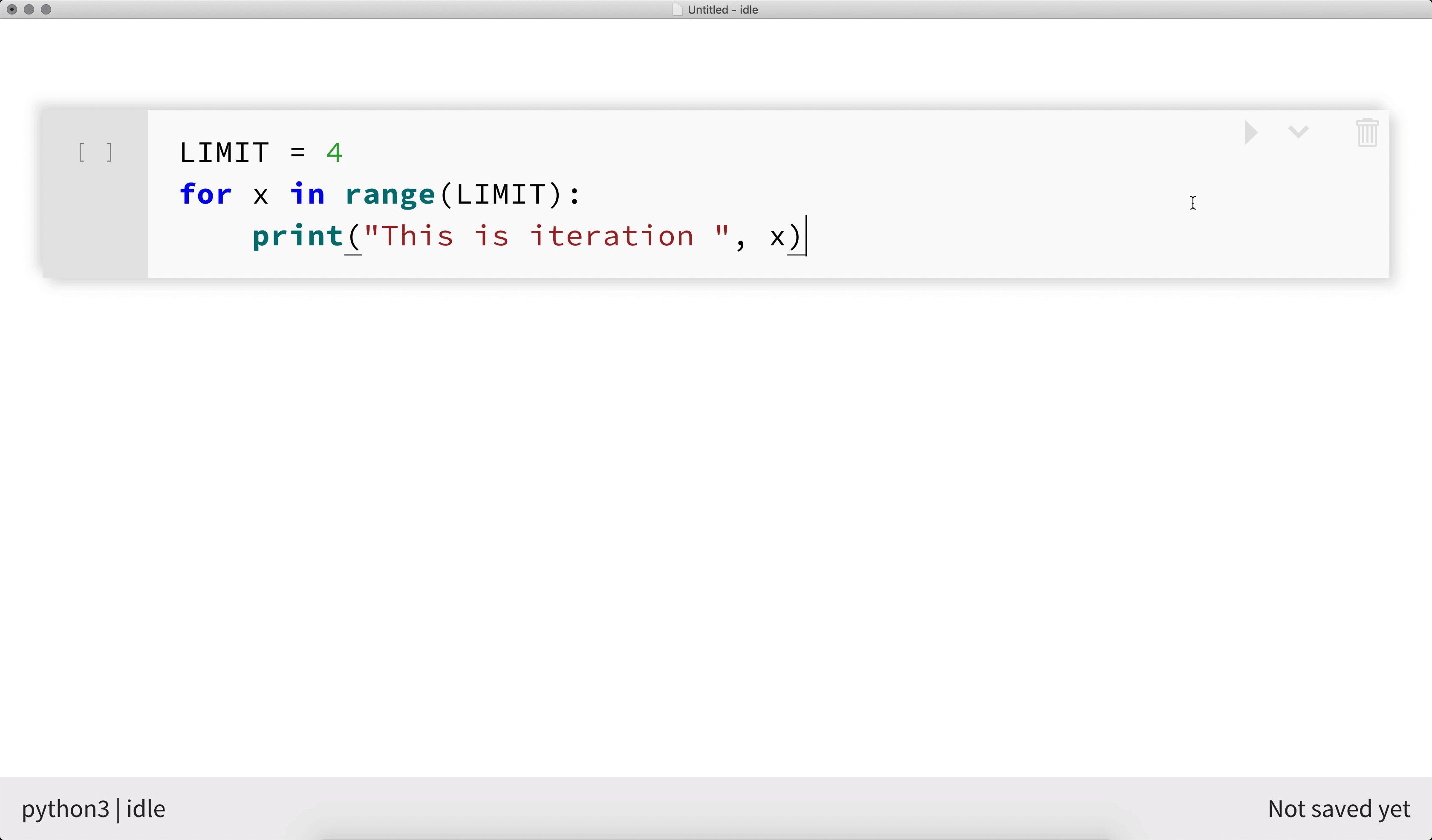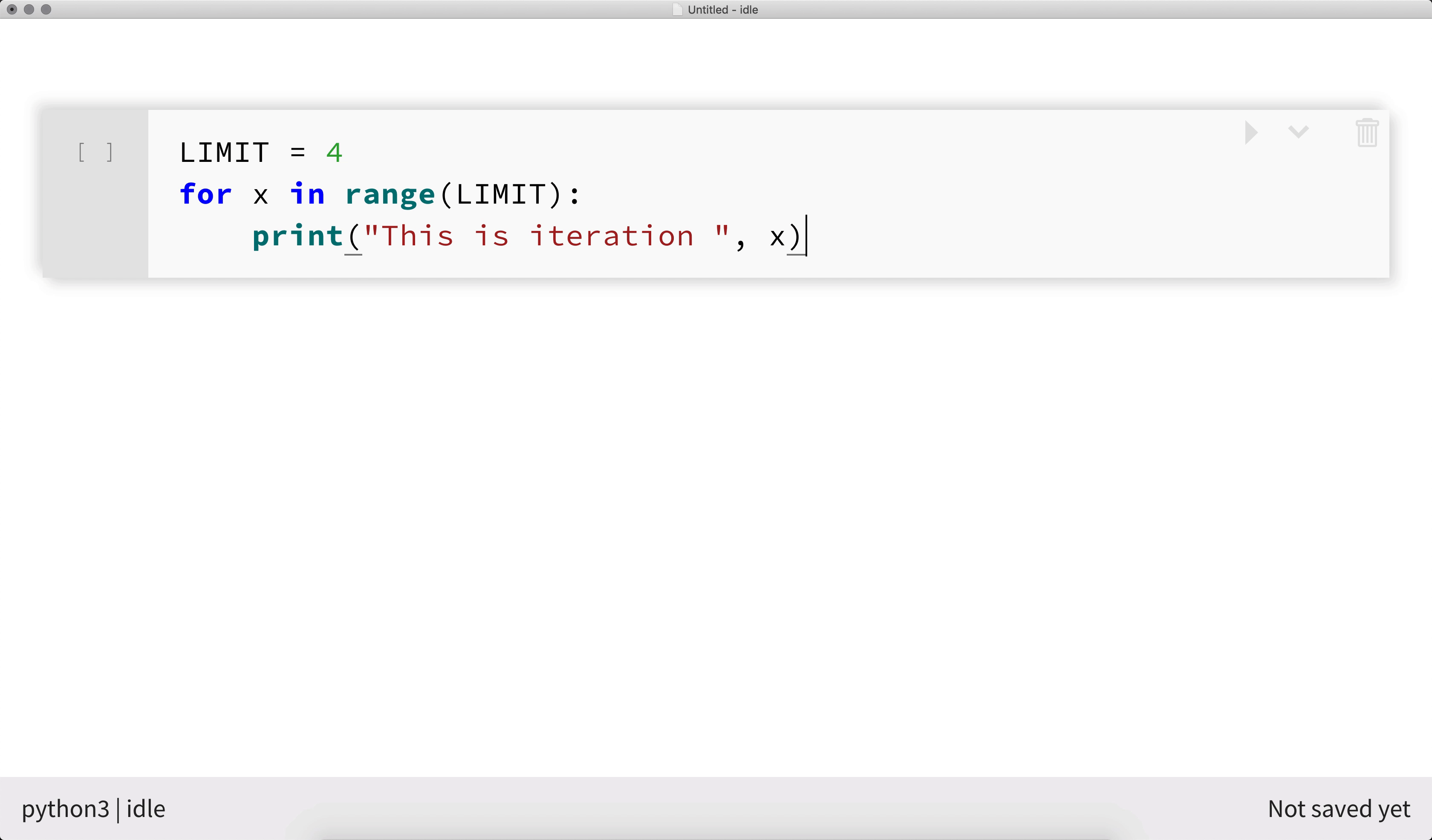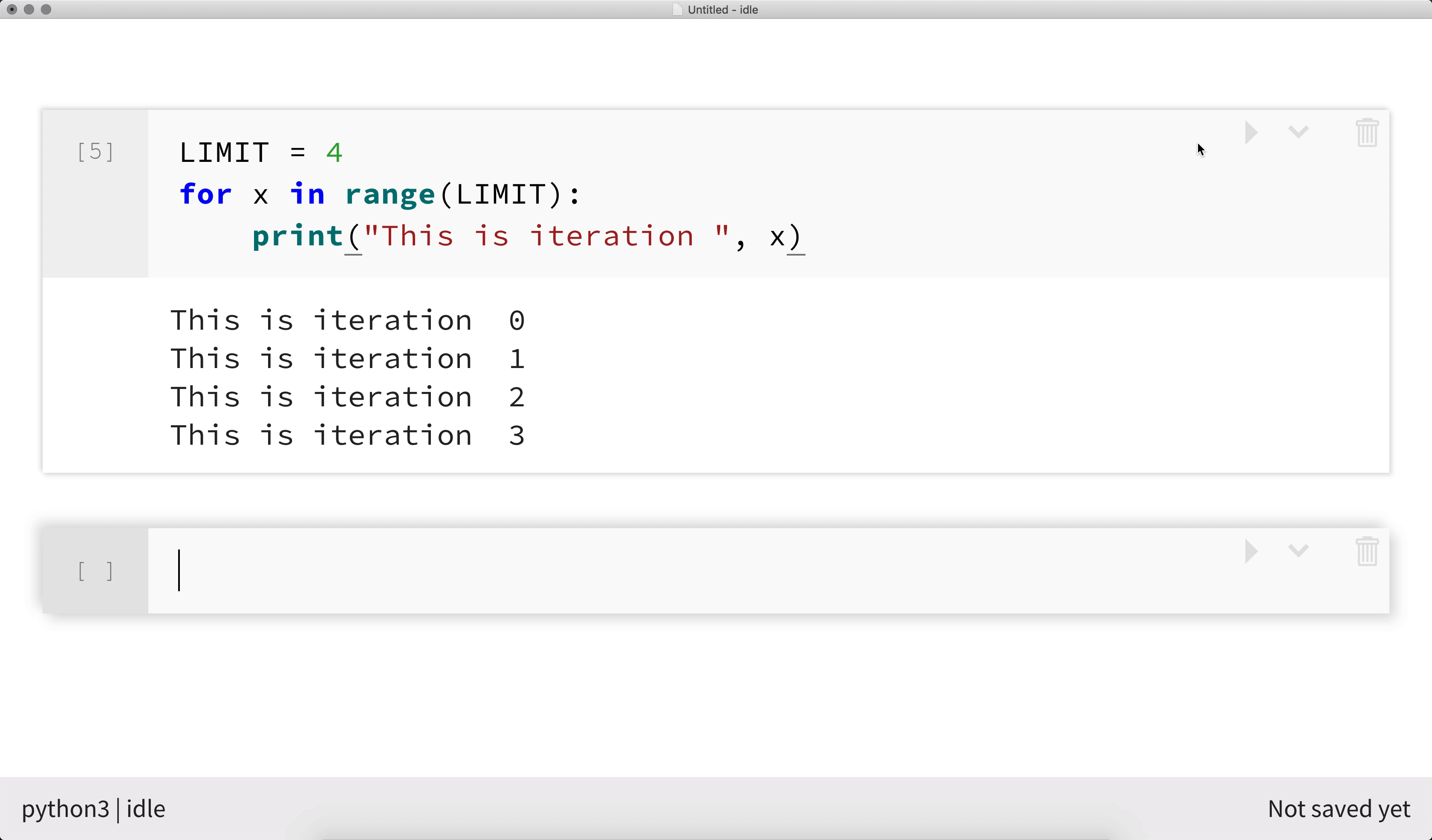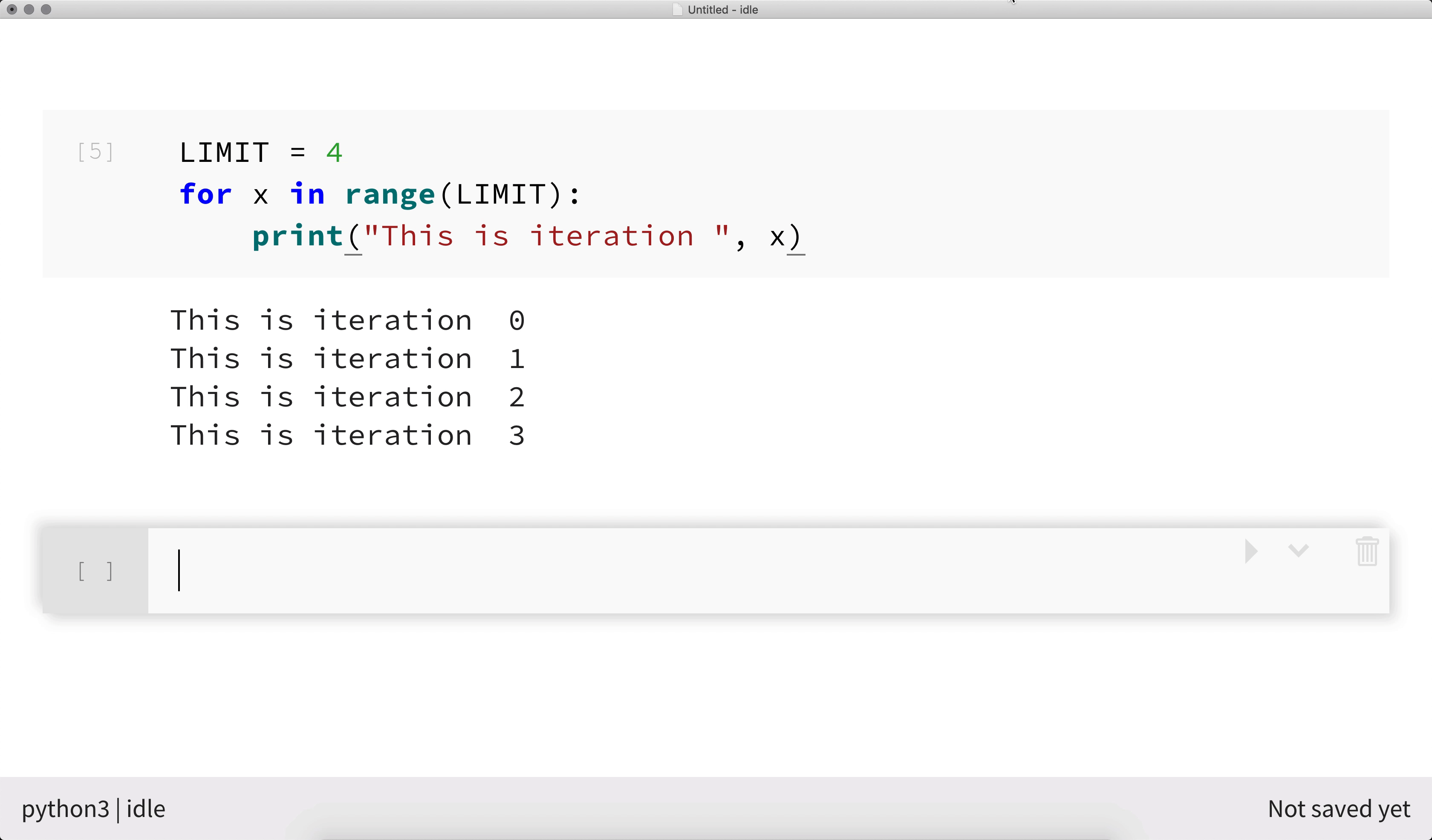
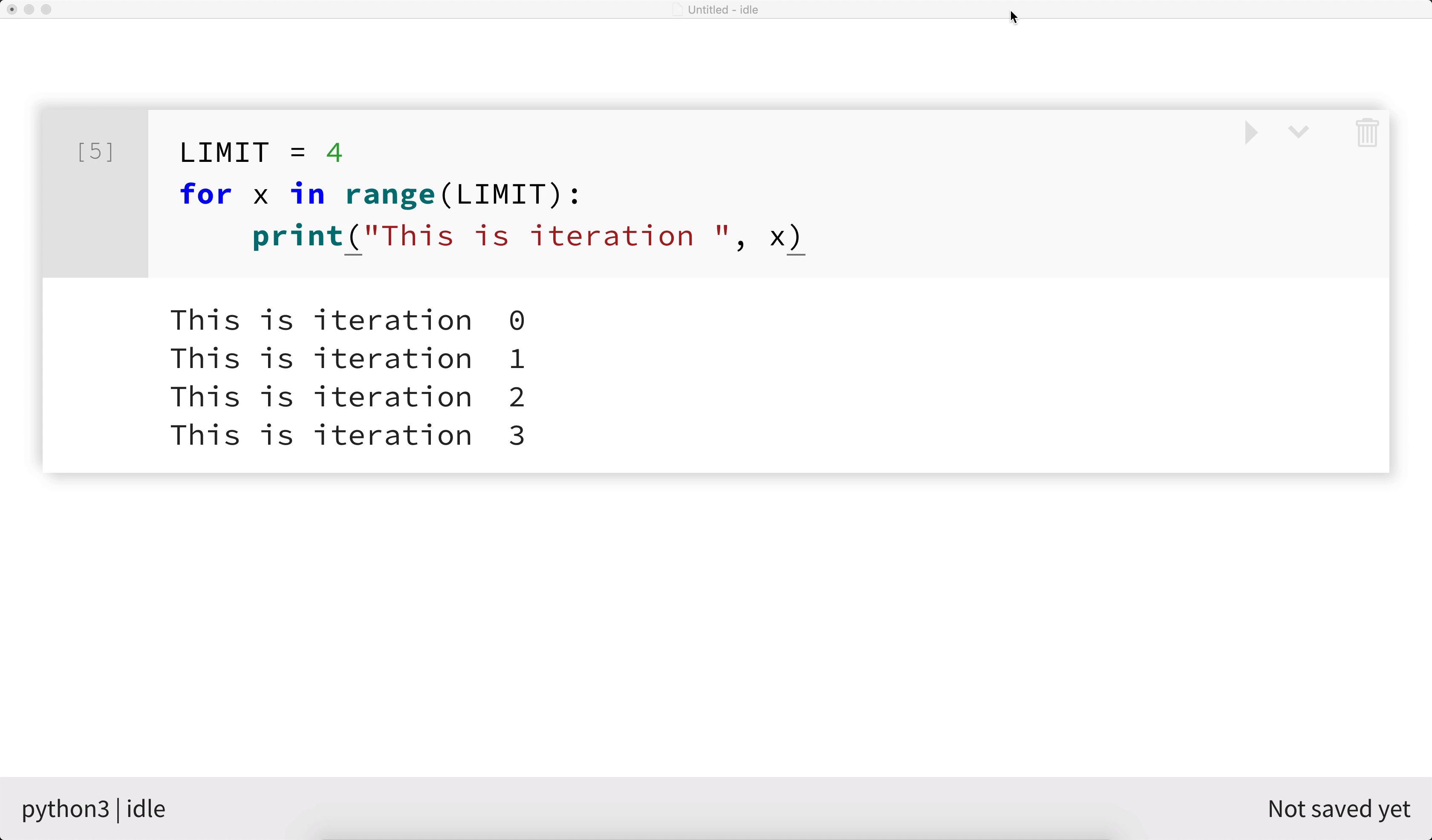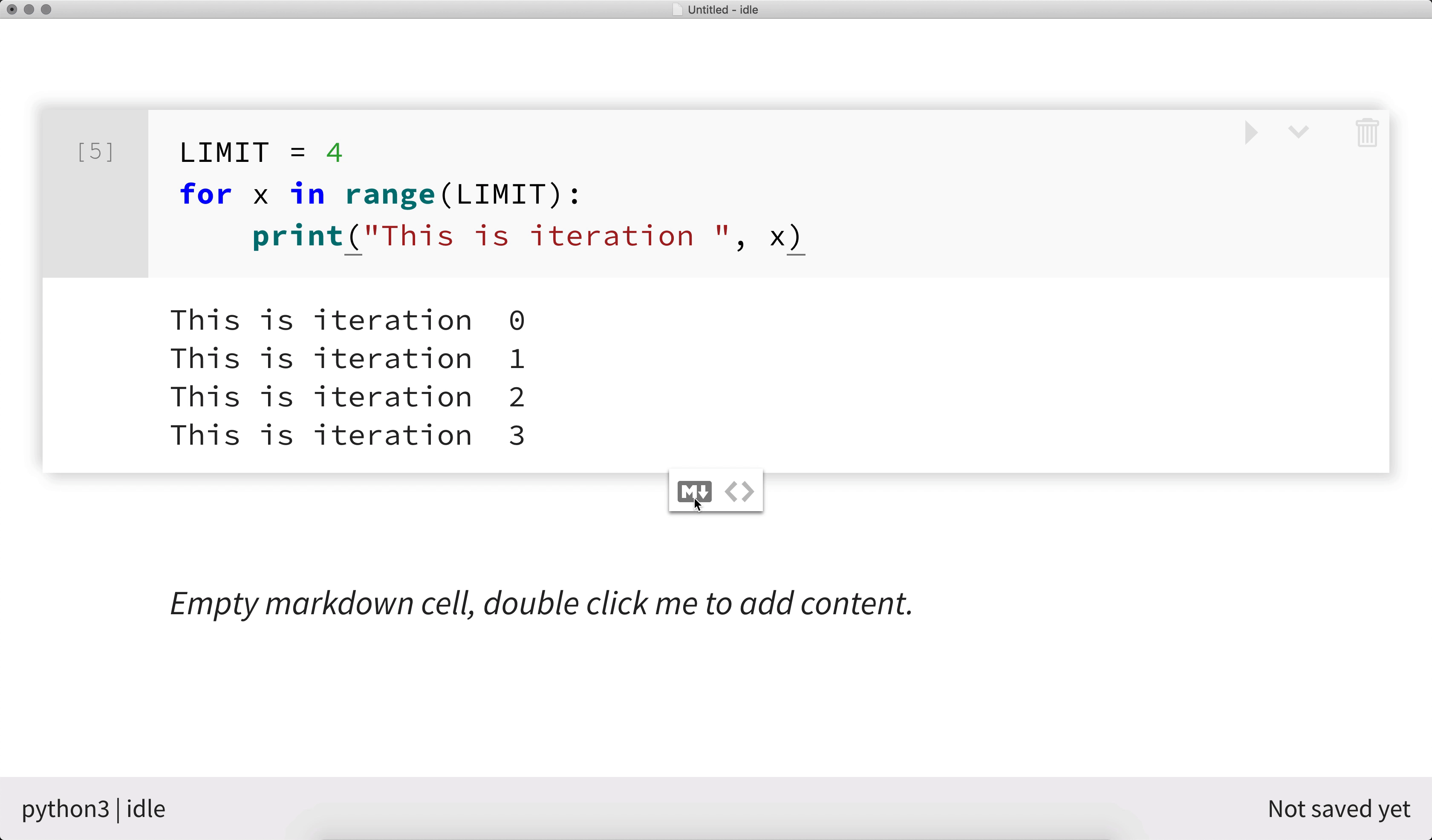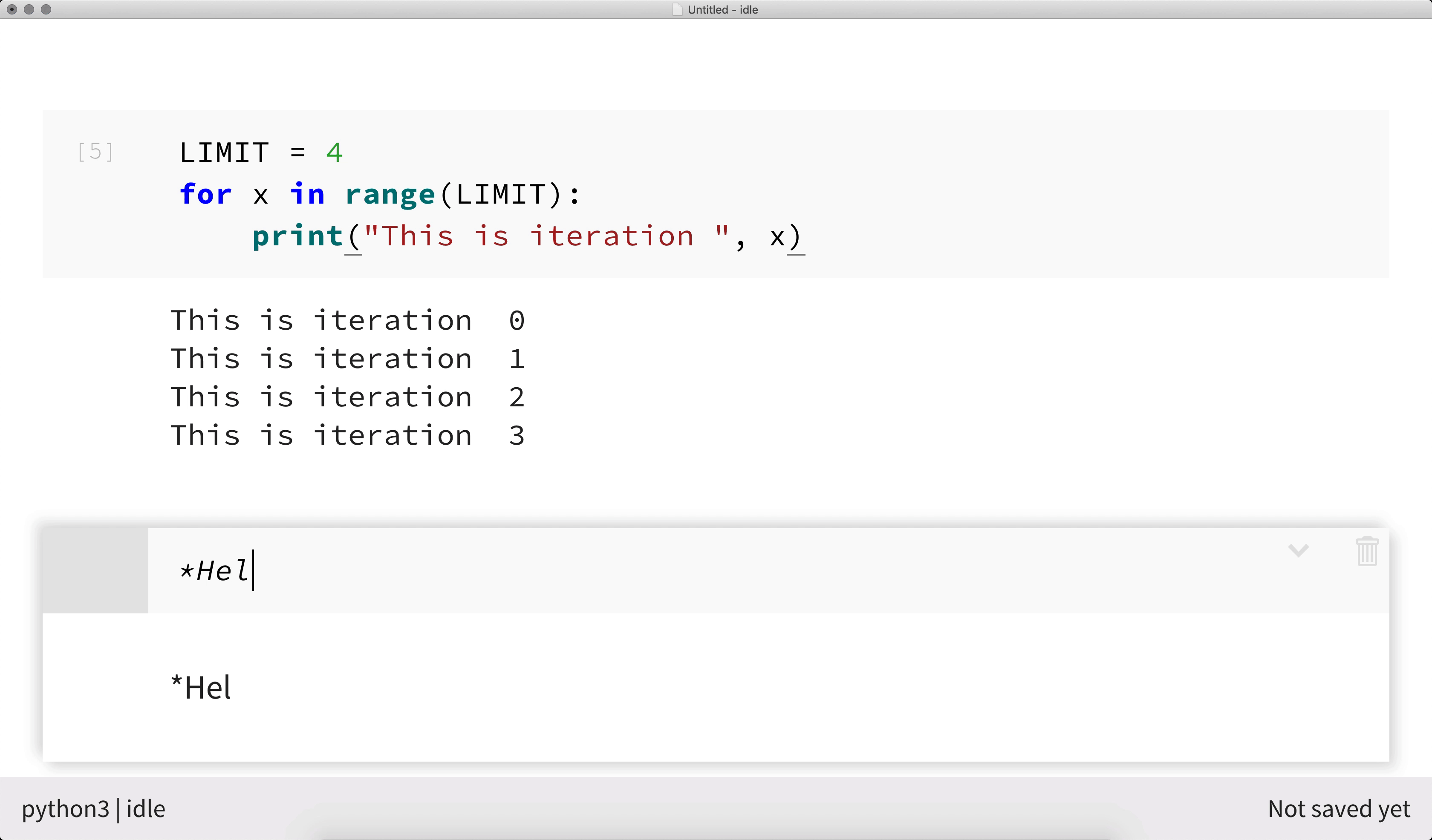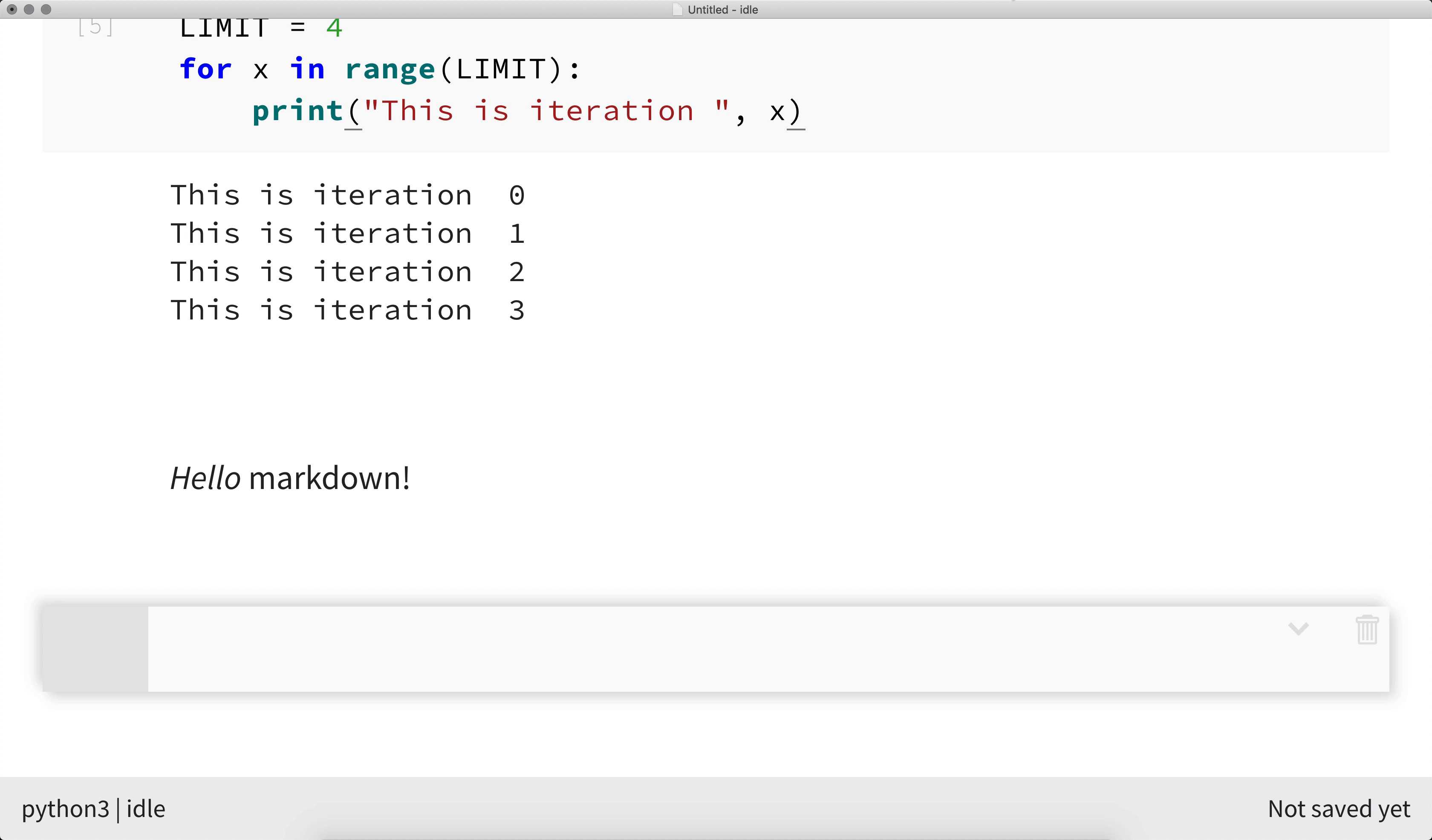
The example below shows Python 3 code executing within an interactive notebook.
Writing documentation in interactive notebooks¶
You can also create textual cells. These provide documentation and narrative for your code. Format textual cells using the Markdown formatting language.
Create a new Markdown cell in the nteract application with these two methods.
- Hover over the space after a cell and click the Markdown icon (the letter M with a down arrow next to it).
- Select Edit > Insert Text Cell Below from the menubar.
After creating a new Markdown cell, double click to edit and write your formatted text content.
Organizing cells within a notebook¶
nteract allows you to rearrange the cells within a notebook using drag-and-drop. Click on the left-hand side of a cell and drag it to your desired position.
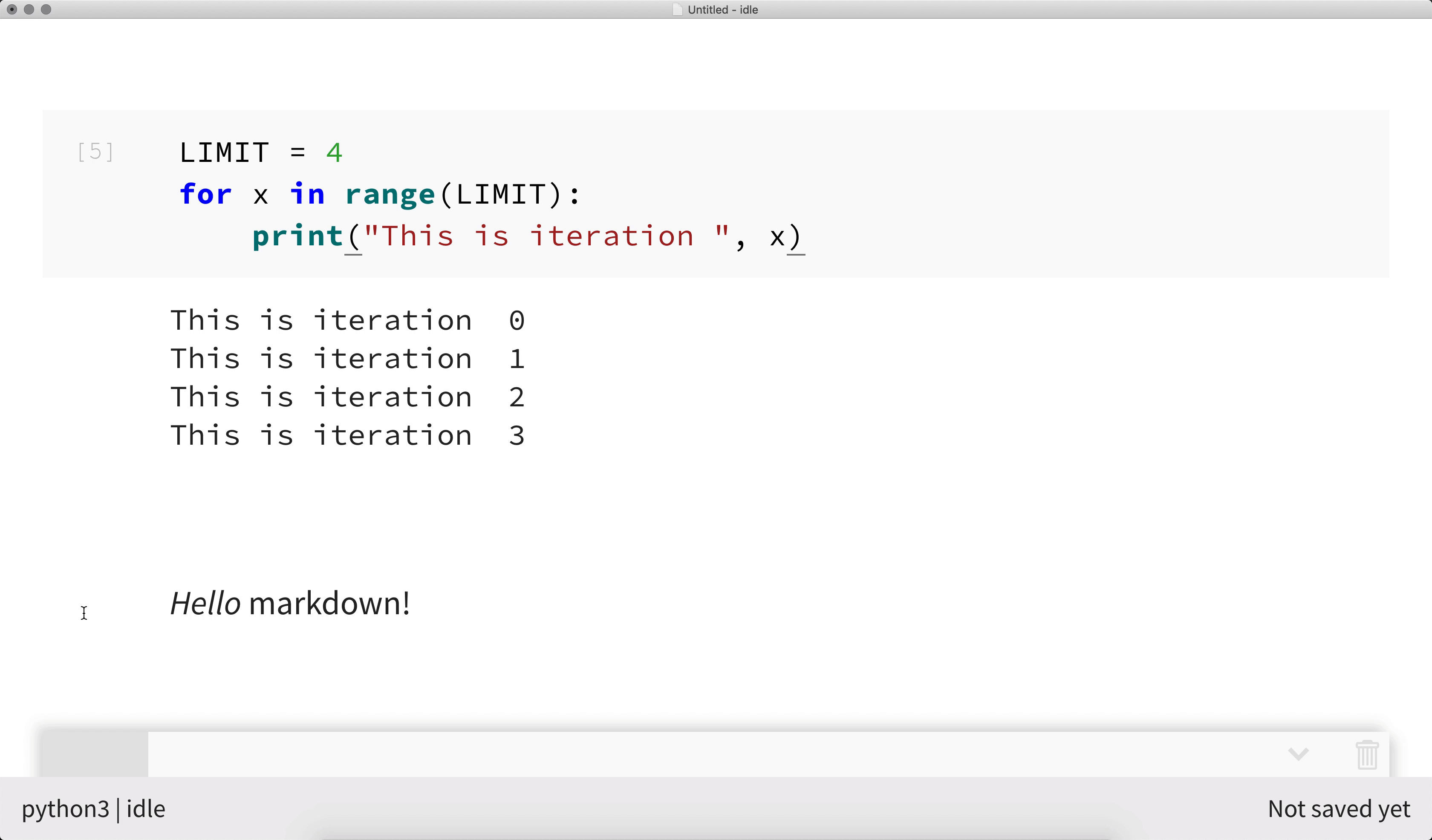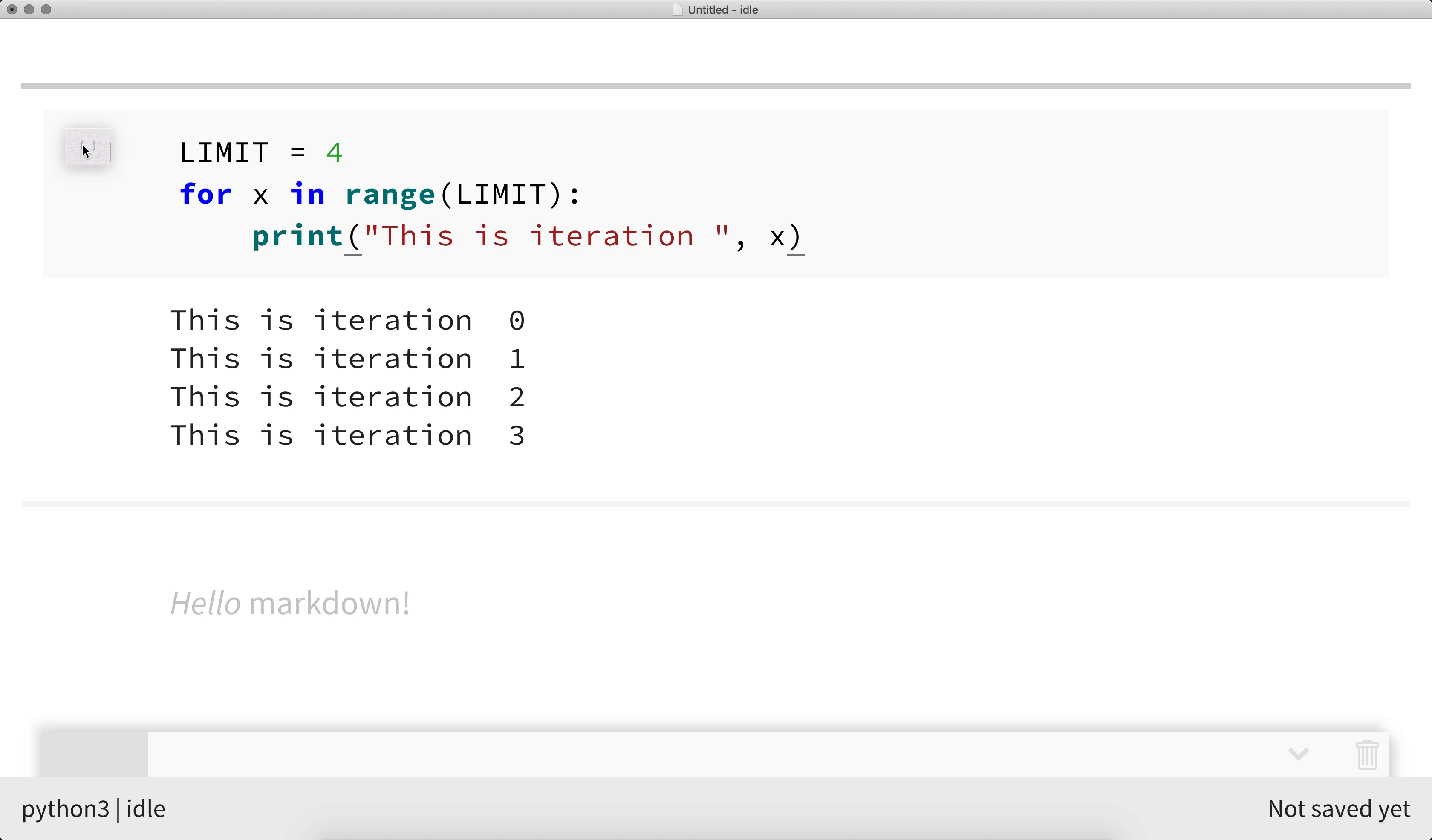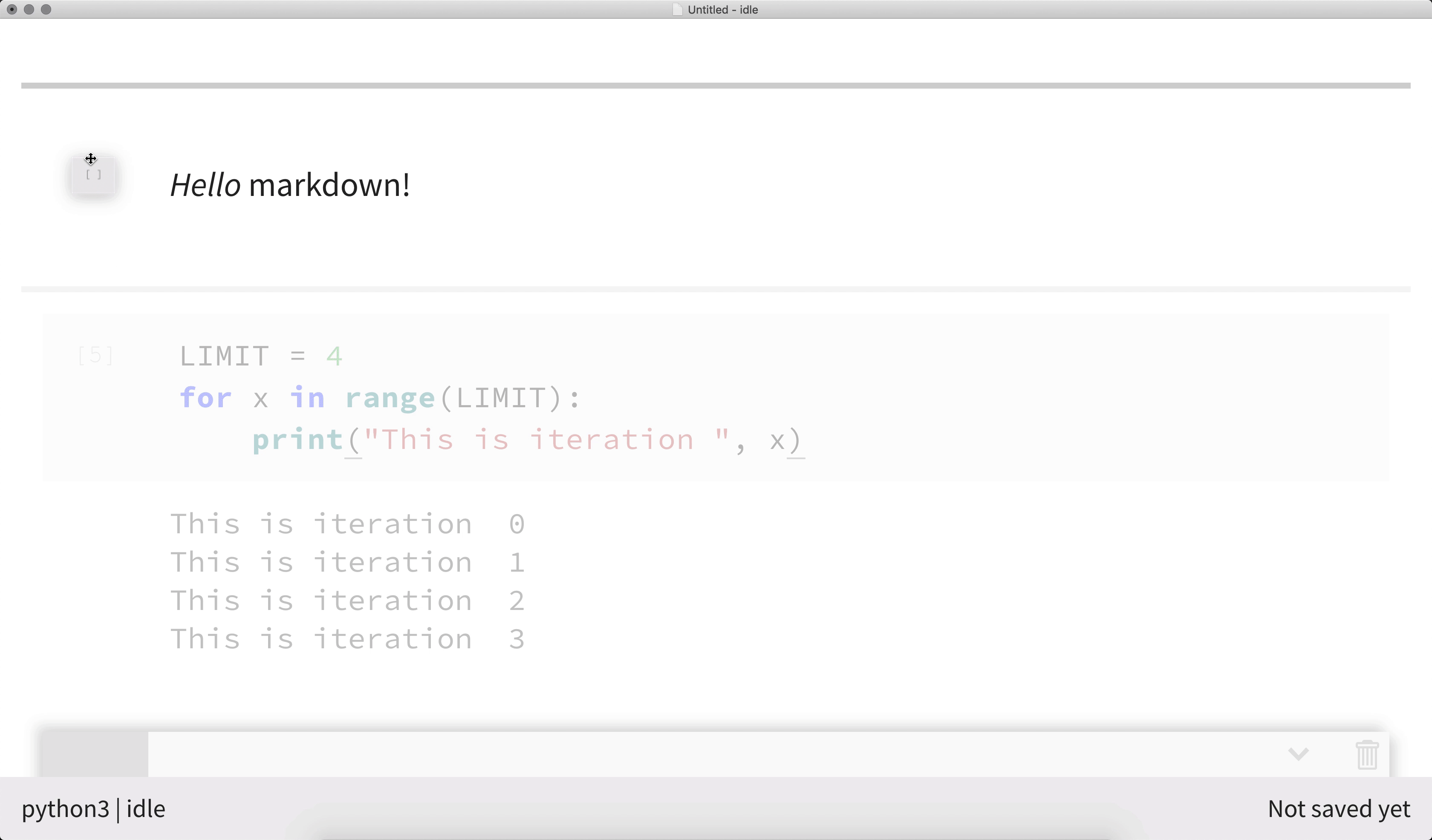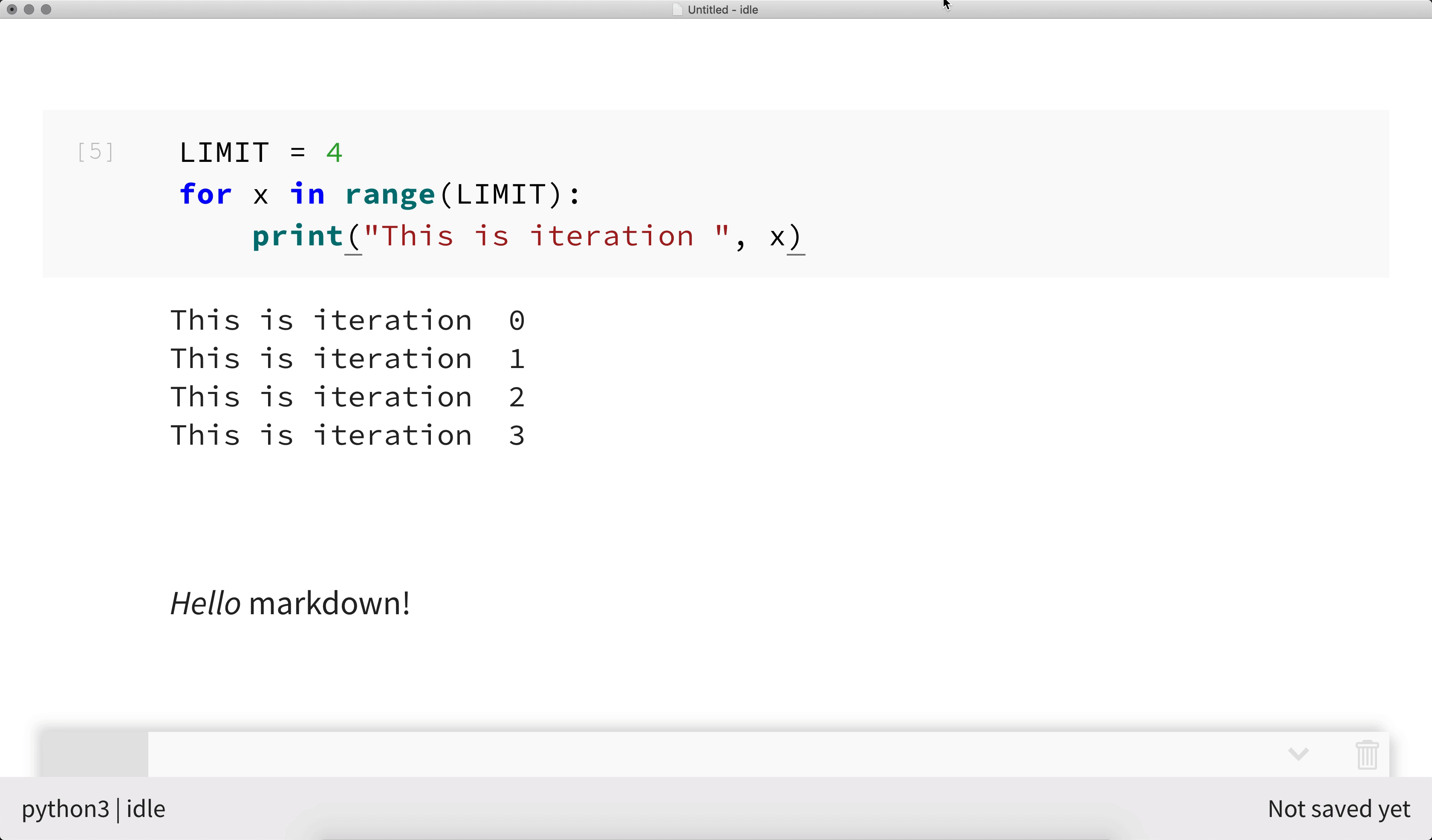
Speed things up with keyboard shortcuts¶
Take advantage of keyboard shortcuts within nteract. Compare the full list of keyboard shortcuts to JupyterLab and classic Jupyter front ends to get started with these keyboard shortcuts.
In addition, see the specific list of cell keyboard shortcuts.
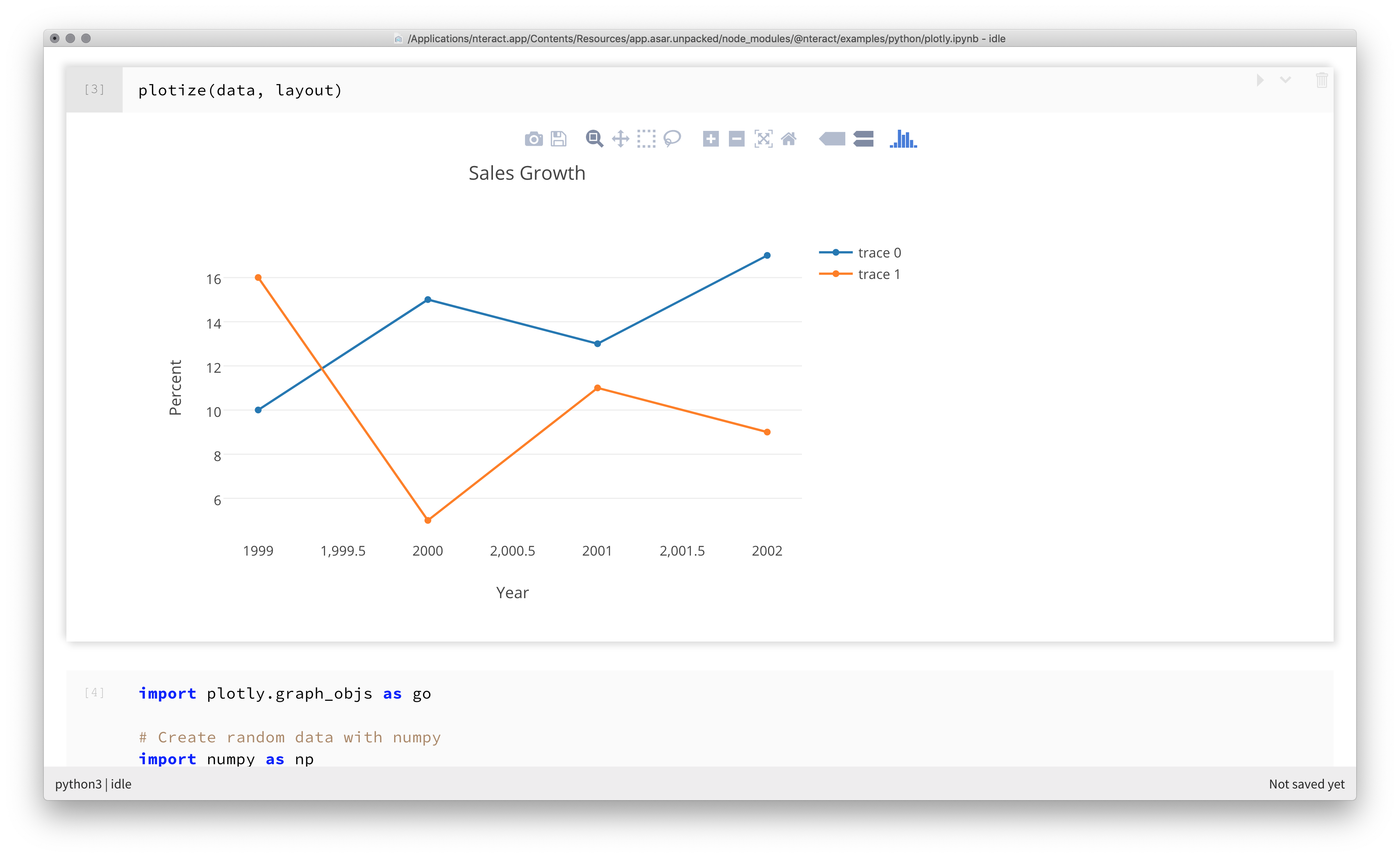
Rendering rich media in interactive notebooks¶
With nteract, render media such as images and maps directly within the notebook. The bundled notebook examples show how this works in nteract.
The steps below demonstrate installing a dependency.
Navigate to File > Open Example Notebook > python > Gallery of Plotly Plots.
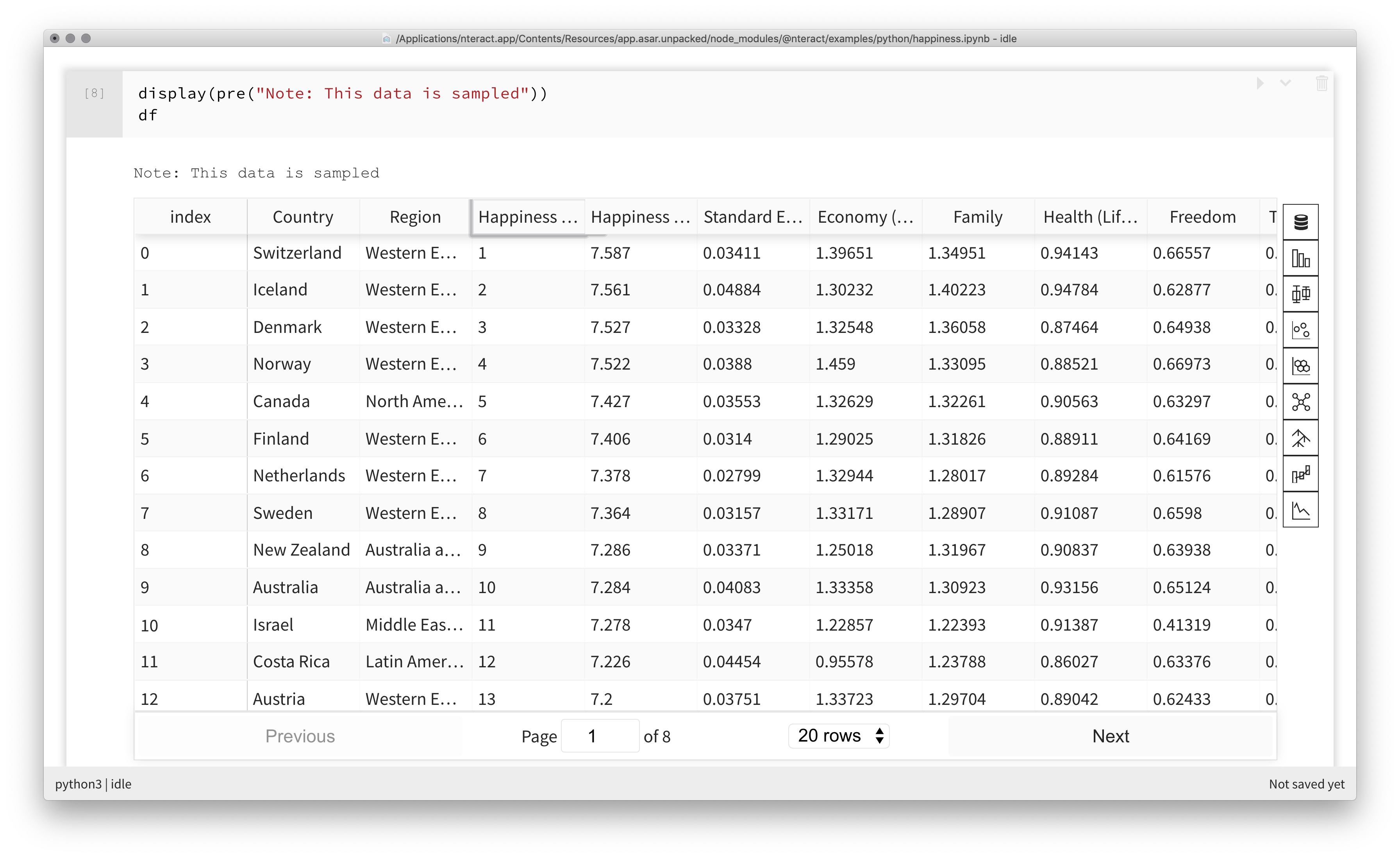
Creating visualizations with the nteract Data Explorer¶
The nteract Data Explorer is a built-in tool for visualizing pandas DataFrames within a notebook.
View an example of the Data Explorer process in nteract.
Navigate to File > Open Example Notebook > python > Try the Data Explorer.
NOTE: By default, the Data Explorer renders the data in a rich, paginated table.
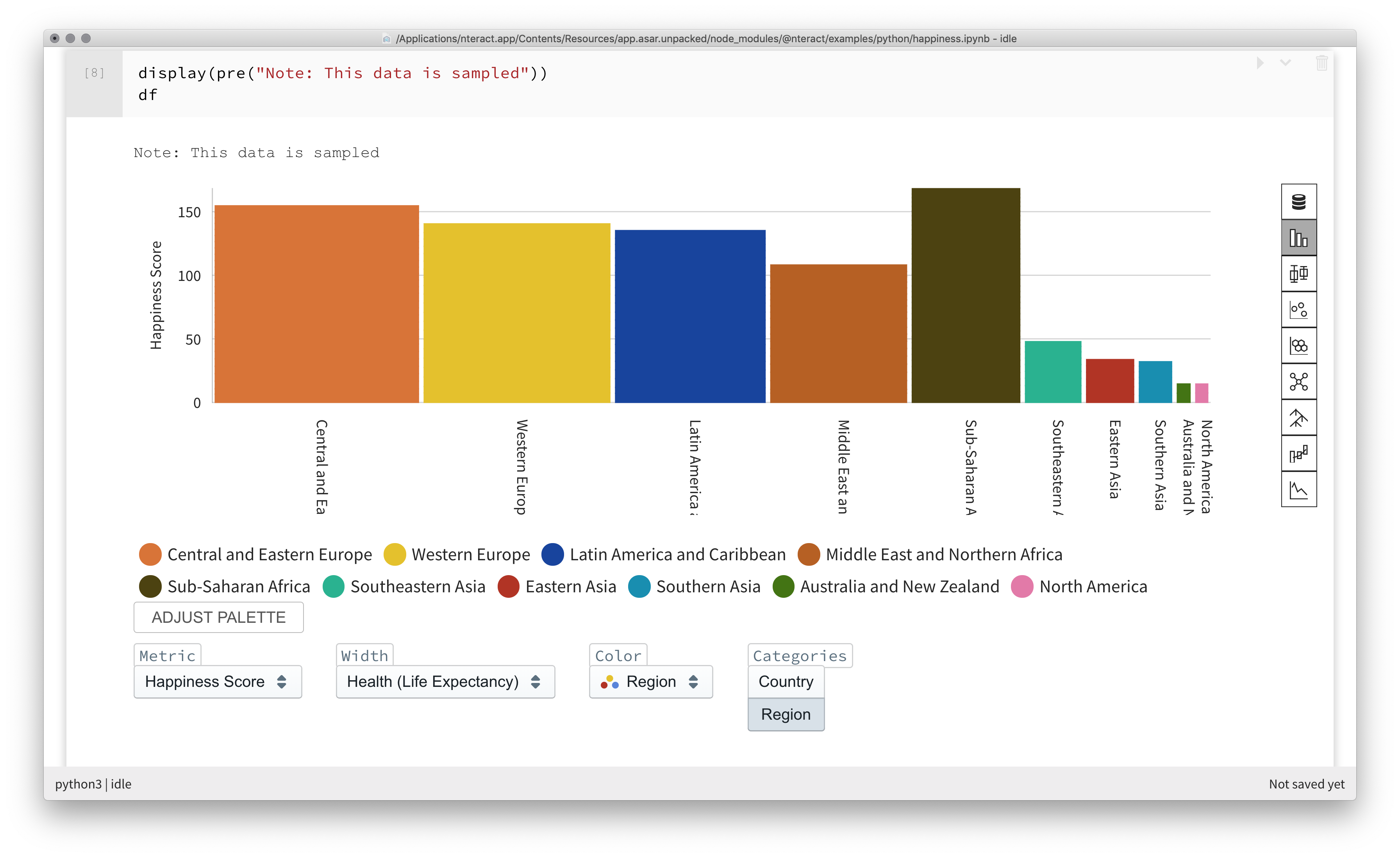
Using the buttons on the right of the Data Explorer, switch to different views of the same data.
The example below shows data from the table categorized and filtered into a bar plot.
Go forth and explore!¶
nteract creates opportunities for you to create all varieties of exciting and compelling notebooks.
Find more example notebooks and features in nteract in the menubar.
Select File > Open Example Notebook
